8.7 KiB
ip2nginx
💡 Project Overview
ip2nginx is a lightweight and secure system for dynamically updating NGINX reverse proxy configurations based on public IP address changes, typically reported by edge devices like pfSense. It ensures that NGINX always routes traffic through the correct IP, even in dynamic environments.
📚 Table of Contents
- 💡 Project Overview
- 🏠 What is ip2nginx?
- 💡 Example Use Case
- ⚙️ Features
- 📁 Project Structure
- 🚀 Update Process: update.php
- 🚀 Update Process: updater.php
- 🛠 Environment Setup: check_env.php
- 📅 Cron Setup with run.sh
- 🔄 Usage Example from pfSense
- ✅ Example Entry in token.json
- ✅ Example Entry in meta.json
- 🛡 Security
- ✅ Requirements
- 📜 License
- 🤝 Author
🏠 What is ip2nginx?
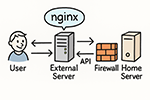
ip2nginx is a self-hosted system that allows you to securely expose services running on your private home network (e.g. NAS, internal web interfaces, or a self-hosted app) under your own domain — without using third-party dynamic DNS services.
Instead of changing DNS records, it updates the reverse proxy (NGINX) configuration on your public server — making it the only point that needs to be publicly reachable. 🔐 Why is this more secure?
Your home server does not need to be exposed to the entire internet. Only your external server (running ip2nginx) needs access. This allows you to:
Restrict incoming firewall access at home to just one remote IP (your public server).
Avoid direct exposure of your internal services to DDOS or scanning attempts.
Offload all public traffic to the external server, preventing your home bandwidth from being overwhelmed.
⚙️ How it works:
Your home gateway (e.g. pfSense or another device) periodically sends its current public IP to your external server using an authenticated API call.
The external server updates only the proxy_pass directive inside a specific location block in the NGINX config for your domain.
NGINX is automatically reloaded to apply the changes.
From the outside world, visitors reach your external server, which transparently proxies to your home server — using your latest IP.
This gives you full control, avoids third-party dependencies, and increases the security of your home infrastructure.
💡 Example Use Case
You want to host https://home.example.com and route it to a web interface at your home (like pfSense or a Raspberry Pi), but your IP changes regularly due to your ISP.
With ip2nginx, the server automatically updates the NGINX reverse proxy so your domain continues working — securely and without dynamic DNS services.
⚙️ Features
- Accepts remote updates via
update.phpusing token-authenticated requests. - Supports both
POSTandGET, though POST is preferred to avoid token caching. - Updates only the
proxy_passline in the relevantlocationblock ofnginx.conf. - Automatically marks entries in
meta.jsonas"changed": 1when input changes. - Logs all changes to
log.jsonwith timestamps. - Automatically reloads NGINX:
nginx -t && systemctl reload nginx(requires root). - Built-in abuse protection: failed requests tracked and blocked.
.htaccessensures that onlyupdate.phpis externally accessible.
📁 Project Structure
ip2nginx/
├── index.php # Shared configuration and fallback error handler
├── update.php # Receives incoming remote IP update requests
├── updater.php # CLI-only: applies changes to nginx.conf if marked
├── run.sh # Wrapper script for cron automation
├── check_env.php # Environment validator and bootstrapper
├── .htaccess # Blocks unauthorized access, routes traffic
├── data/
│ ├── meta.json # Stores current configuration state per domain
│ ├── token.json # Stores allowed tokens (auth)
│ ├── log.json # Stores audit log of changes
│ ├── blocklist.json # Temporarily blocked IPs (48h ban)
│ └── failures.json # Tracks failed attempts per IP
🌐 Remote Update API: update.php
Supports POST (preferred) and GET methods.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
✅ | Identifier (e.g. domain1.to.com) |
token |
✅ | Secret token assigned for this name |
ip |
❌ | New public IP (default: auto-detected from request) |
domain |
❌ | Backend domain to proxy to (default: same as IP) |
port |
❌ | Port number (default: 443 for https, 80 for http) |
protocol |
❌ | One of http or https (default: https) |
Any change in ip, domain, port, or protocol triggers "changed": 1 in meta.json.
If any parameter is received via GET, then ip and domain will be overridden with the client’s real IP for security.
🧩 Update Process: updater.php
To apply updates made via update.php:
- Load all entries from
meta.json - Check for entries marked
"changed": 1 - Find
/var/www/vhosts/system/<domain>/conf/nginx.conf - Modify the appropriate
locationblock’sproxy_passdirective only - Validate and reload NGINX
- Reset
"changed": 0
🛠 check_env.php: Environment Setup
This CLI script validates:
- Config files and permissions
- JSON structure of each config file
- Auto-creates missing files (with defaults)
- Token file includes example if missing
⏱ Cron Setup: run.sh
To automate updates, add run.sh to your crontab as root:
sudo crontab -e
Then add:
*/5 * * * * /path/to/ip2nginx/run.sh
This ensures automatic application of proxy changes to NGINX config and reloads.
🔄 pfSense Shell Example
Add the following script to pfSense via System > Advanced > Cron:
#!/bin/sh
SERVER="https://your-server.com/ip2nginx"
NAME="domain1.to.com"
DOMAIN="domain.from.com"
TOKEN="YOUR_SECRET_TOKEN"
curl -s -X POST "$SERVER/update.php" -d "name=$NAME" -d "domain=$DOMAIN" -d "protocol=https" -d "port=443" -d "token=$TOKEN"
✅ Example: token.json
{
"domain1.to.com": "SECRET_TOKEN_8v73jDKsdLzAq9DkeUz1",
"domain2.to.com": "SECRET_TOKEN_3im83jUj28mjo2mI23un"
}
✅ Example: meta.json
{
"domain1.to.com": {
"domain": "domain.from.com",
"ip": "192.0.2.4",
"port": "443",
"protocol": "https",
"location": "/",
"time": "2025-05-16T09:00:00+00:00",
"changed": 1
}
}
🔒 Security Highlights
.htaccessdenies access to all files exceptupdate.php.- Only HTTPS connections should be used.
- All tokens are stored securely and verified per name.
- After 3 failed attempts, IP is banned for 48 hours.
- Generic error messages avoid leaking details to attackers.
✅ Requirements
- PHP 7.4 or newer
- NGINX with reload access (
sudo systemctl reload nginx) curlon the client side- Token definitions in
token.json
📜 License
MIT (or similar): Open-source, free for use and modification.
🤝 Author

**Maintained by SAFE-CAP / Alexander Schiemann / https://safe-cap.com**